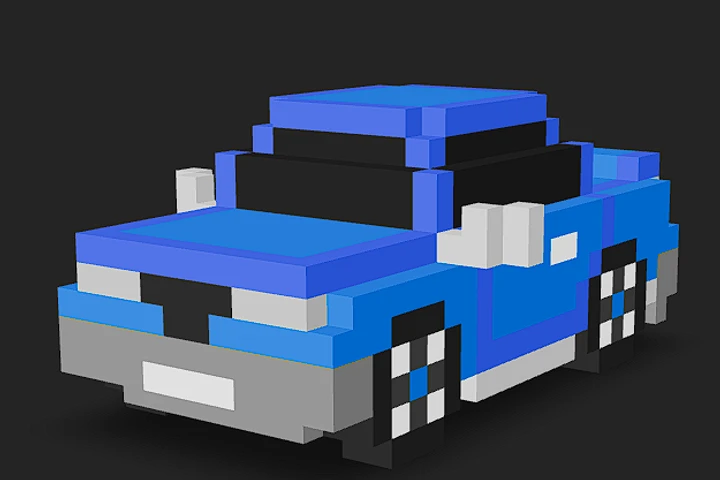
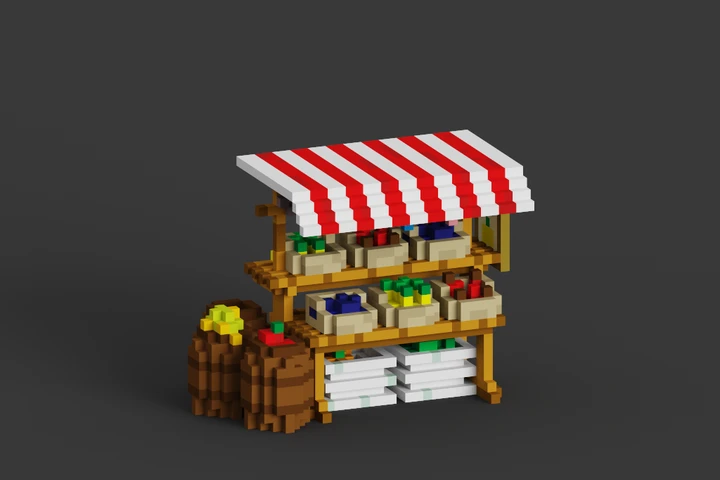
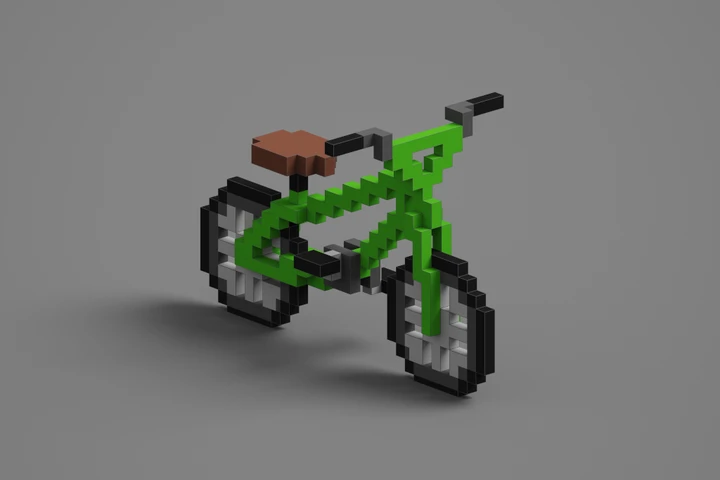
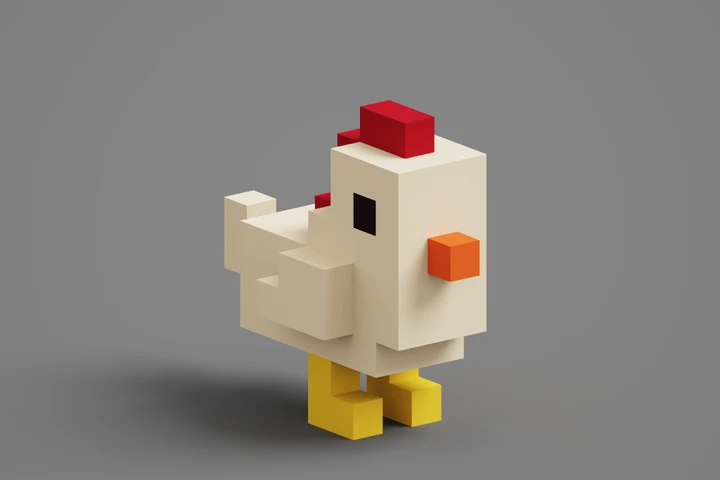
Welcome to VoxBox
A MagicaVoxel asset sharing platform
Easily upload, share and download MagicaVoxel .vox assets. Whether you're looking to inspire or be inspired, VoxBox is the perfect platform for creators of all levels.
- Sign up for FREE – create a VoxBox account for free and start sharing and rating other people's creations
- Browse and filter – search through various assets in 8 different categories.
- Realtime 3D & AR viewer – view all magicavoxel models instantly in your browser, both on desktop and mobile. AR preview available on certain platforms!
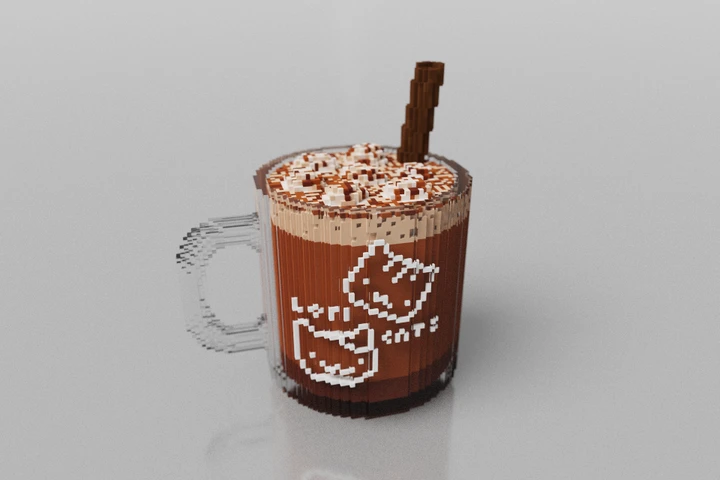
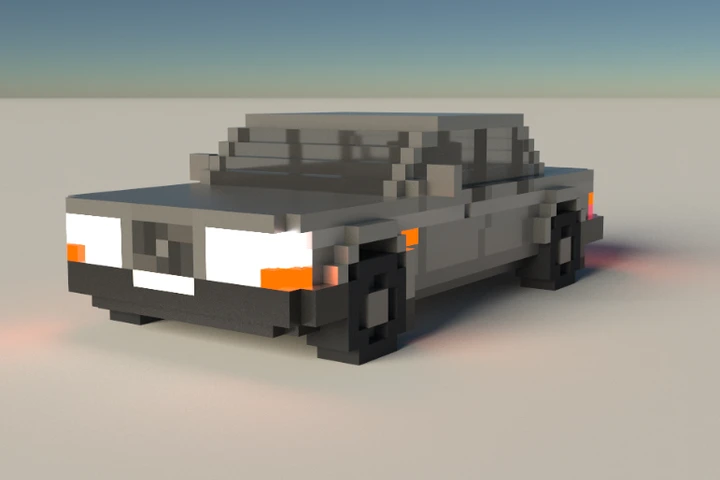
Featured Models
Check out the current hand-picked featured models!
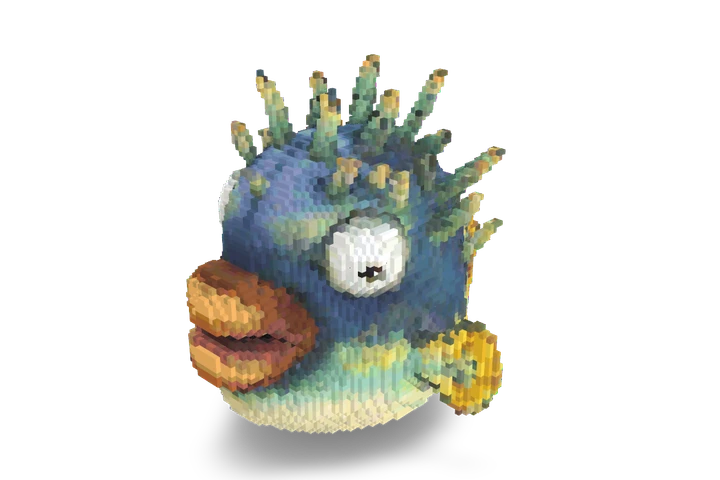
Latest Models
Here are the latest models uploaded by the VoxBox community.
New to voxels?
Here's all you need to know to get started!
So what is a "voxel model"? A voxel model is a type of 3D digital model that represents objects using a grid of volumetric pixels, known as "voxels." Unlike traditional 3D models that use polygons to define surfaces, voxel models define objects in a blocky, pixelated form, similar to 3D pixels.
Voxel art key characteristics:
- Grid based structure – Voxel models are composed of a three-dimensional grid where each cell, or voxel, represents a small, cubic unit of space. Each voxel has a specific position in the grid and can store data such as color, density, or material type.
- Resolution and Detail – The detail in a voxel model depends on the resolution of the grid. Higher resolution grids contain more voxels, allowing for finer details. However, this also increases the complexity and memory usage of the model.
- Solid Representation – Unlike surface-based models, voxel models inherently represent volume. This means that they naturally handle complex geometries, like overhangs or internal cavities, which can be challenging for polygonal models.
- Editing and Interaction – Voxel models can be easily edited by adding or removing voxels, which is akin to placing or deleting small blocks in space. This makes them intuitive for certain types of creative tools and applications.
- Rendering and Performance – Rendering voxel models can be computationally demanding, especially at high resolutions, but they allow for efficient, dynamic modifications and interactions, making them popular in scenarios requiring real-time editing.
Video made by: PremiumBeat by Shutterstock